Content Retrieval and Finder Tool
Content Retrieval and Finder Tool
| Developer | Jordy Kafwe |
|---|---|
| Year | 2024 |
| Platform | Web-based |
| Type | HTTP API |
Resources
Project Aims
The project aimed to break down technical barriers that made it difficult for people to contribute to and benefit from Abstract Wikipedia. It focused on making it easier to find and understand what data exists in Wikidata, which is important for creating constructors. The project sought to create an HTTP API that would accept constructors, fetch relevant data, and perform query expansion to suggest related items, helping users discover more about what is available in Wikidata. Designed as an HTTP API, CRAFT aimed to ensure easy integration with other applications in Abstract Wikipedia. These efforts were intended to make it easier for a wide range of users to engage with and contribute to Abstract Wikipedia.
Features
Parser for Processing Constructors
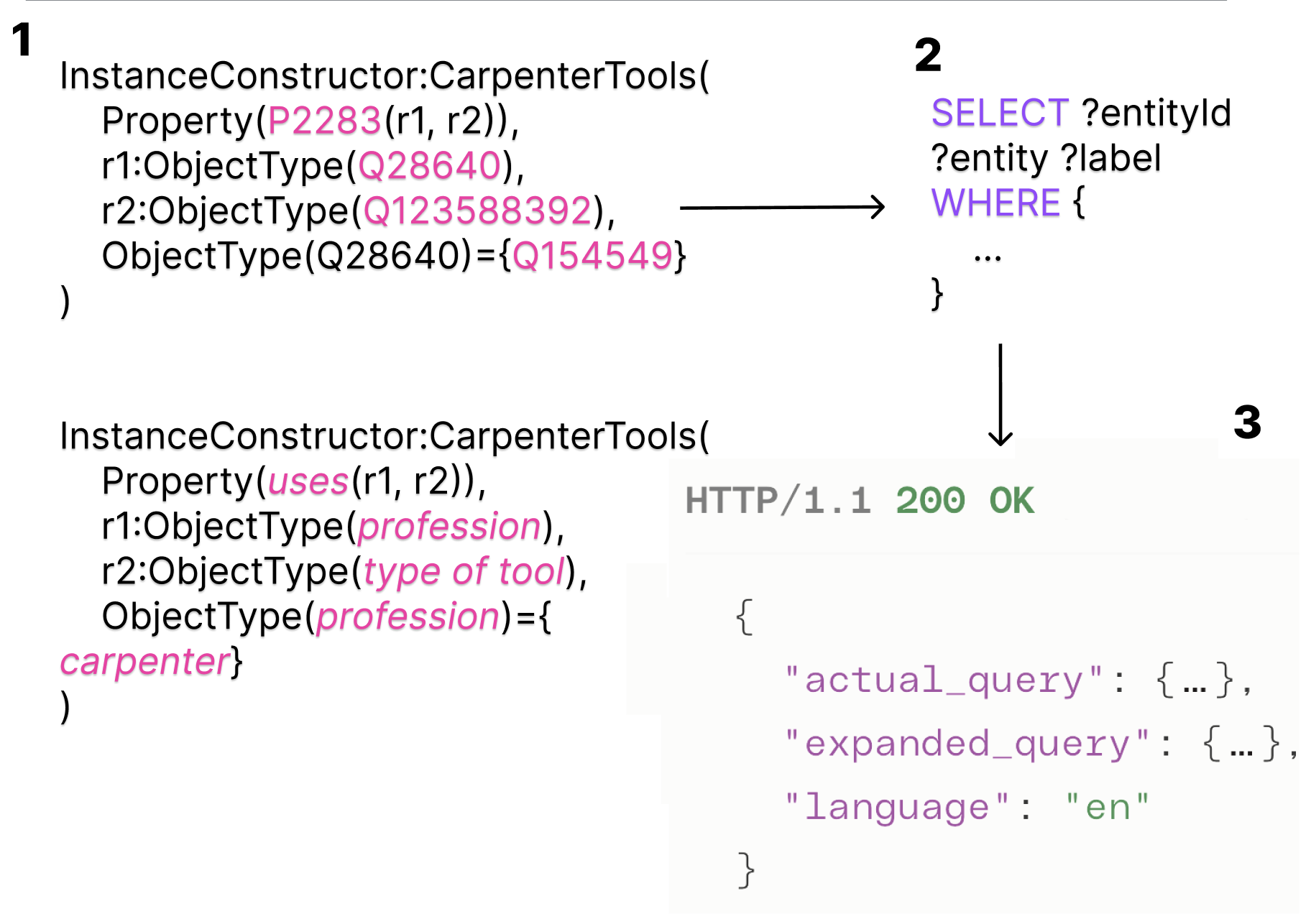
The CRAFT API includes a parser that interprets CoSMo constructors, converting them into queries for content retrieval from Wikidata. The parser is built is using ANTLR which helps ensure accurate transformation of content representations into actionable queries.
Handles Multilingual Input and Returns Content in the Input Language
CRAFT processes input in multiple languages and returns content in the same language. It uses language identifiers to map constructs to language-specific data in Wikidata, supporting Abstract Wikipedia's multilingual content goals.
Query Expansion for Related Content Suggestions
To enhance content discoverability, CRAFT implements query expansion by suggesting related content. It fetches nodes connected to the entity of interest in Wikidata, prioritising widely used information to provide broader context.
JSON Response with Selected Content for Use in Other Abstract Wikipedia Apps
The API delivers content in a structured JSON format, facilitating integration with other Abstract Wikipedia applications. This ensures efficient data exchange and reuse across project components.
System Architecture
The architecture of the CRAFT API is designed to efficiently handle multilingual content selection. It uses a layered approach, which enhances modularity, scalability, and maintainability. Each layer is responsible for a specific function.
HTTP API Layer
The HTTP API layer serves as the mediator between the user and the backend system. It receives CoSMo statements via HTTP requests and coordinates the processing of these statements through the various layers of the system. Upon receiving a request, the API layer first invokes the Parser Layer to interpret the CoSMo syntax. It then calls the Semantic Analysis Layer to ensure the constructs are semantically valid. Next, the Mapping Layer is engaged to translate these constructs into SPARQL or SQL queries. The combined Execution and Result Processing Layer executes these queries against the appropriate database, retrieves the requested data, and formats it into a JSON response. This orchestration ensures that data, and potentially related data, is fetched accurately and efficiently, supporting the integration of Wikidata information into Abstract Wikipedia articles.
Parser Layer
The Parser Layer is responsible for interpreting CoSMo constructors. Using ANTLR, it converts these high-level representations into a parse tree. This layer ensures that the input is syntactically correct and ready for further processing.
Semantic Analysis Layer
This layer performs semantic checks on the parsed constructs to ensure their validity and coherence. This mainly involves checking that variables are not used before they are declared.
Mapping Layer
The Mapping Layer translates CoSMo constructs into SPARQL queries. It maps the parse representations to the appropriate data structures in order to generate a SPARQL query.
Execution and Result Processing Layer
This combined layer handles the execution of the generated queries against the target database and formats the retrieved data into a structured JSON response. It interfaces with RDF triple stores for SPARQL queries, ensuring that the data retrieved is consistent with the specifications outlined in the CoSMo constructors. The formatted JSON response is then ready for integration with other Abstract Wikipedia applications, supporting seamless content reuse and display.
Algorithms
Query Generation
The algorithm for generating queries begins with the parse tree produced by the parser, which represents a parsed CoSMo constructors. We then use the ANTLR Listener pattern to traverse the tree in a depth-first manner, processing each node. During this traversal, data structures such as lists and dictionaries are used to store information necessary for constructing RDF triples. Lists are used to accumulate these triples and dictionaries map CoSMo variables to their types. These RDF triples encapsulate the subject, predicate, and object relationships derived from the CoSMo statements. Once the triples are constructed, they are used to assemble the final SPARQL query, ensuring that type constraints are applied to match specified types.
Query Expansion
The query expansion algorithm enhances content discoverability by fetching nodes directly connected to the entity of interest. It uses a SPARQL query to retrieve properties and values associated with the entity, ordering results by the number of sitelinks. A higher number of sitelinks suggests that the information is widely used across Wikimedia projects. This approach helps users discover significant and commonly referenced attributes of the entity, providing a more comprehensive overview of its characteristics and associations. The algorithm prioritises data with more sitelinks, ensuring that users receive the most relevant and widely recognised information.