AfriLex is a specialized lexicographical database designed to enhance Wikidata's coverage of Niger-Congo B languages, including Bantu, by facilitating the collection, refinement, and batch upload of linguistic data. AfriLex stands out due to its unique design, which is specifically tailored to accommodate the linguistic complexities of the Niger-Congo B languages. This focus on the Niger-Congo B language family ensures that the platform is finely attuned to the intricacies and nuances of these languages, providing a rich and accurate representation of their grammatical structures, phonology, and vocabulary. This specialized design is a testament to AfriLex's commitment to delivering a platform that is not only functional but also culturally sensitive and linguistically accurate. Another notable feature of AfriLex is its integration of advanced technological tools to enhance its functionality. For instance, the platform includes a SPARQL query endpoint, which enables users to perform complex searches and extract specific linguistic data efficiently. This feature is particularly useful for researchers and linguists who require precise and targeted information. Additionally, AfriLex boasts a verb form generator, which can automatically generate various forms of verbs based on the linguistic rules of the Niger-Congo B languages. This feature is invaluable for language learners, educators, and linguists, as it provides a quick and reliable means of understanding verb conjugations in these languages.
Wikidata, which is a free and open knowledge base that anyone can edit .One of its standout features is its emphasis on language-independent data. This means that Wikidata is designed to store information in a manner that is not tied to any specific language. As a result, data can be accessed, edited, and utilised by individuals from diverse linguistic backgrounds. Despite its stature as a prominent knowledge base, Wikidata exhibits a notable deficiency in lexicographical data for numerous African languages, particularly those belonging to the Niger-Congo-B family. This shortfall becomes particularly conspicuous when assessing the lexemes, the fundamental lexical units of a language, available for these languages in comparison to more globally recogniSed languages. For example, as of 2022, the Zulu language, a member of the Niger-Congo B family, accounted for a mere 1,000 lexemes on Wikidata, in stark contrast to English which boasted over 400,000. Such stark imbalances underscore the prevalent underrepresentation of African languages on international platforms like Wikidata. Such a gap in accurate representation adversely affects projects that depend on Wikidata as a foundational resource, such as Abstract Wikipedia.
AfriLex aims to enhance Wikidata's coverage of Niger-Congo B languages by providing a comprehensive and linguistically detailed lexicographical database.
We designed our Niger-Congo B languages database through an iterative cycle, starting with a review of relevant resources and projects. This informed the creation of an initial ORM prototype, which encapsulated key linguistic features. The prototype was then refined based on additional analyses, ensuring accuracy and comprehensiveness while reducing the risk of failure and simplifying development.
The database captures the complexity of Niger-Congo B languages through interconnected entities. LanguageFamily and Language categorize languages, connecting to linguistic details like Morpheme and Phoneme. Word entries are displayed through the Word entity, linked to a central LexicalEntry. Tonal intricacies are represented by TonalPattern and Tone entities, while User, VerbForm, VerbalMorphology, and VerbExtension entities handle user management and grammatical complexities, among others.
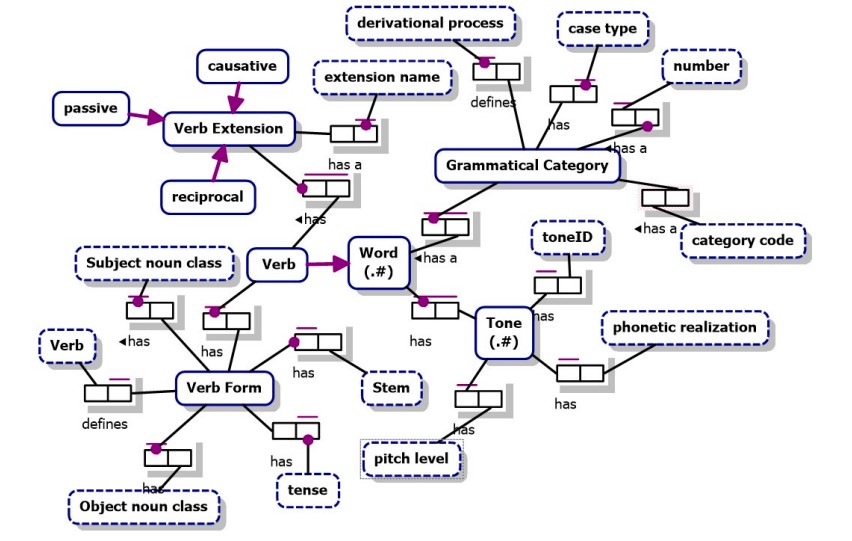
The AfriLex Database Application is a modular and scalable platform specifically designed for storing and managing lexicographical data of Niger-Congo B languages. It features a comprehensive database that encapsulates the linguistic intricacies and grammatical features of these languages. The application leverages MySQL for efficient data management, and employs a lightweight Python Flask backend coupled with a dynamic JavaScript frontend to provide a responsive user interface. Key features include a custom bot, WingUCTBOT, for batch uploading data to Wikidata, a SPARQL endpoint for enhanced data querying capabilities, and a unique Verb Form Generator that automates the generation of diverse verb forms, ensuring the linguistic diversity of Niger-Congo B languages is accurately represented and easily accessible.





The project successfully improved the representation of Bantu Languages on Wikidata, achieving a high upload success rate of 99.26%.
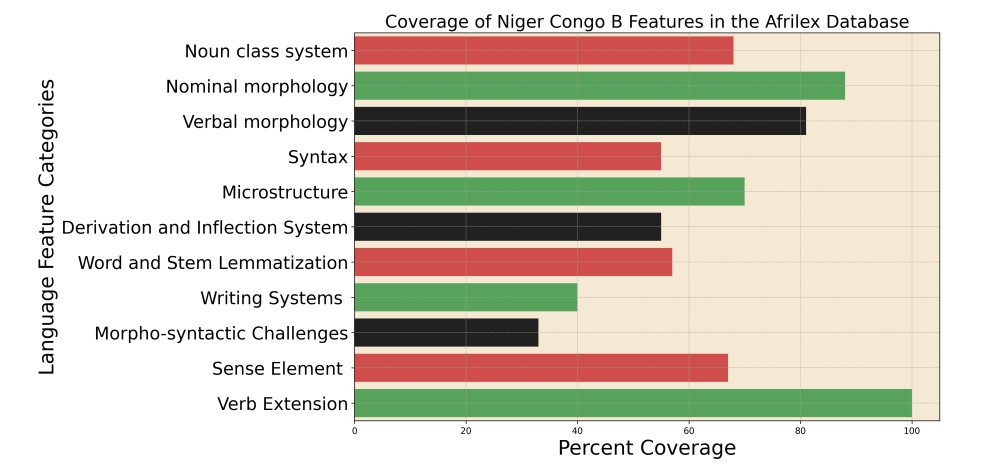
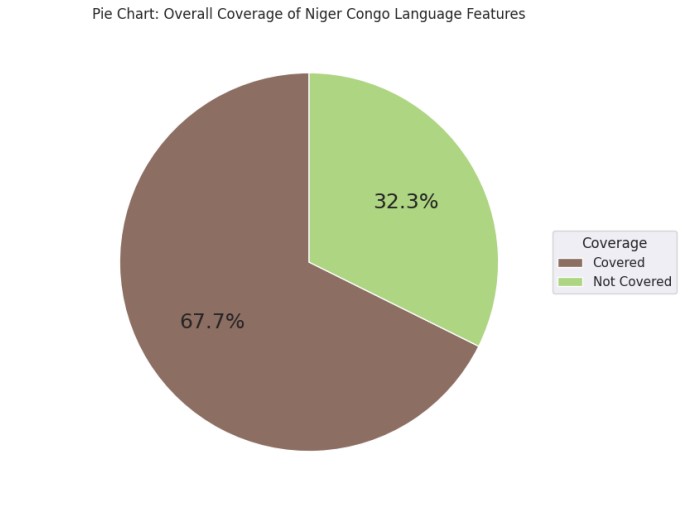
Below are the results based on our project objectives to improve Wikidatas lexicographic repository for Niger Congo B Languages. The evaluations carried out provide insights into the data compatibility, linguistic representation, and the performance of the Verb Form Generator. The findings highlight our project's achievements and point towards areas for further improvement.